Yeast collection and reuse is a long-established practice in brewing. With proper yeast handling and repitching practices, brewers can effectively reduce yeast expenses by maintaining yeast health and reusing a single strain for multiple generations and many batches of beer.
Brewing schedules are crucial to help maximize efficiency and ensure the yeast is not left in storage too long. Harvesting yeast is relatively easy to implement. All that is needed is a sterile storage vessel, cold storage space, and a solid SOP with good practice.
- Collecting and harvesting yeast at the optimal point of fermentation will avoid prolonged exposure to yeast stressors in the fermentor, ensuring healthy yeast harvests.
- Proper cold storage with minimal exposure to oxygen can extend the viability and shelf life of yeast from batch to batch.
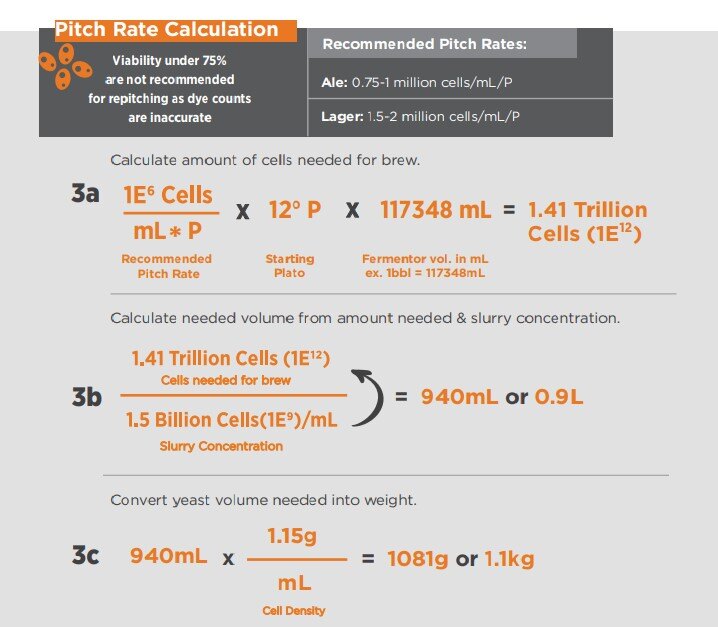
- Differences in pitching rate can affect flavor production, fermentation speed, yeast health, and flocculation, leading to yeast harvesting problems. Pitching the right amount of yeast is key to reliable fermentations and a great-tasting beer every time.
These methods can reduce yeast price points from $50/bbl (single use) to $2/bbl (multiple generations) with minimal investment, labor, or supplies.
Simply tracking the culture lineage and fermentation kinetics will provide outstanding results in beer quality and your bottom line.
- Schedule harvest during mid-to-end fermentation.
- Apply 3-5 psi of head pressure to the fermentor.
- Attach tri clamp, tri clamp gasket, and tri clamp hose adapter to valve on conical fermentor. Attach sanitized tubing to tri clamp hose barb adapter.
- Slowly open valve to discard trub until healthy yeast slurry is visible. Close the valve and connect sanitized tubing to yeast brink or storage vessel.
- Slowly open the valve until the healthy yeast slurry is seen flowing into the storage vessel. Be sure to monitor harvest speed to avoid potential tunneling of yeast in the conical fermentor. Harvest yeast until the entire slurry is collected or target volume is achieved.

- Transfer the brink to a cold environment, ideally between 36-39°F (2-4°C)
- Vent the storage vessel daily in order to maintain good yeast viability and vitality.
- Minimize oxygen exposure and storage time to preserve yeast health for subsequent repitches; ideally, only store for 1-3 days.
*If storing longer periods (7-14 days or more) verify yeast viability before repitching.
- Transfer the brink to a cold environment, ideally between 36-39°F (2-4°C)
- Vent the storage vessel daily in order to maintain good yeast viability and vitality.
- Minimize oxygen exposure and storage time to preserve yeast health for subsequent repitches; ideally, only store for 1-3 days.
*If storing longer periods (7-14 days or more) verify yeast viability before repitching.

- Remove yeast vessel from cold storage and place on scale.
- Measure weight of slurry, excluding keg weight.
- Calculate the required slurry volume if the cell concentration of stored yeast slurry is known. (See formula below)
- Apply 3-5 psi of head pressure to storage vessel.
- Attach tri clamp, tri clamp gasket, and hose from valve on conical fermentor or hard line to storage vessel.
- Slowly open valve to push yeast slurry into fermentor
- Allow yeast to fill vessel until calculated weight/volume has been reached from the storage vessel.