Fermenting a High Gravity beer is always challenging endeavor due to high levels of alcohol, which are toxic to yeast cells, and monstrous amounts of sugars for the yeast to consume. This can lead to stuck fermentations, fusel alcohol off-flavors, and other problems. We dug deeper into brewing a >25 Plato beer to find out the best way to get a proper fermentation.
The Variables
The fermentation standard conditions will be:
- Pitch rate: 1 million/mL/°P
- Fermentation temperature: 20 °C
- Wort: 22 and 25 Plato
- Ferments done in duplicate 1L Flasks
Oxygen was tested with five different profiles:
- No oxygenation
- Under-oxygenation (7 ppm)
- Recommended oxygenation (14 ppm)
- Extra oxygenation (>20 ppm)
- Recommended aeration with oxygen before inoculation, plus extra aeration every 24h for the first three days
The nutrient of FANMax Bio™ were tested with three different profiles w/ recommended aeration:
- Recommended dosage (50 g/BBL)
- 3X recommended dosage (150g/BBL)
- Recommended dosage before inoculation, and extra additions every 24h for the first three days
In fermentations with WLP001 California Ale Yeast®, the addition of FANMax Bio® reduced the time to final gravity by around 50% in both 22 and 25 Plato wort (Fig 1), while maintaining nearly identically pH profiles. Furthermore, despite the faster fermentation, the FANMax Bio® addition didn’t change the final ethanol content (Fig. 2).

 Figure 1. Attenuation and pH curves for WLP001 in a) 25 Plato and b) 22 Plato wort. Nutrient addition contributes to faster fermentation but is particularly impactful in higher gravity.
Figure 1. Attenuation and pH curves for WLP001 in a) 25 Plato and b) 22 Plato wort. Nutrient addition contributes to faster fermentation but is particularly impactful in higher gravity.
 Figure 2. Final ethanol content of the high gravity fermentations.
Figure 2. Final ethanol content of the high gravity fermentations.
Similarly, the impact of the nutrients and oxygenation was tested in WLP099 Super High Gravity Ale Yeast. As observed previously, the addition of FANMax Bio® significantly increased the fermentation (Fig. 3), and final gravity was achieved up to 20 days earlier.
As expected of WLP099, the final attenuation exceeded 80%. Once again, there was almost no difference between the fermentations with different oxygenation profiles, suggesting a low impact of oxygenation in the freshly propagated WL yeast performance.
The FANMax Bio® showed a stronger pH drop in the early days of fermentation but presented a similar final pH. All fermentations presented similar final Ethanol content (Fig. 4).
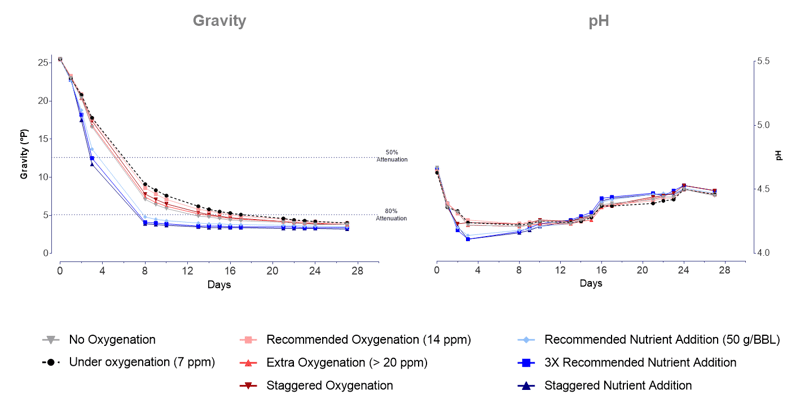
 Figure 3. Attenuation and pH curves for WLP099 in two independent trials in > 25 Plato wort. Nutrient addition contributes to faster fermentation, reducing by 50% the time to final gravity.
Figure 3. Attenuation and pH curves for WLP099 in two independent trials in > 25 Plato wort. Nutrient addition contributes to faster fermentation, reducing by 50% the time to final gravity.
 Figure 4. Final ethanol content of the high gravity fermentations.
Figure 4. Final ethanol content of the high gravity fermentations.
Impact on Fermentation Performance
The addition of FANMax Bio® presented a significant impact on the fermentation performance of WLP001 (Fig. 1) and WLP099 (Fig. 3). Quickening fermentation timelines and reaching terminal gravity in record time meaning faster high ABV beer with a clean fermentation profile. Both the recommended dosage and the three times dosage quickened attenuation rates. We recommend using the normal FANMax Bio® dosage rate of 50g/BBL and only use the 3X recommended dosage (150g/BBL) when necessary as it can partially impart nutrient flavors into the beer.
Surprisingly, the different oxygenation profiles tested had little to no impact on the attenuation curves, including the non-aerated wort. This suggests freshly propagated WL yeast contains the necessary reserves for successful fermentation when inoculated at the recommended pitch rate. Overall, the effects of FANMax Bio® addition in high gravity fermentations are significant and should be widely recommended.
An all-organic version of nutrients, FANMax Bio®, is excellent for providing the necessary nutrients and nitrogen needed for healthy fermentations.
This product contains peptone and yeast extract that provides essential fatty acids, free amino nitrogen, nucleic acids, vitamins, and minerals for your yeast.
An excellent product for deficient nitrogen fermentations such as kombucha, wine, or cider.
FANMax Bio® contributes around 30ppm of FAN for a dosage of 100g/bbL. We recommend using traditional finings agents for most fermentations. If you are still struggling with unwanted haze, filtration may be necessary.











